Type 2 Cytokines
in
Different
Diseases
View the Unique and Overlapping Roles of the Key Cytokines When Type 2 Inflammation Drives Disease1
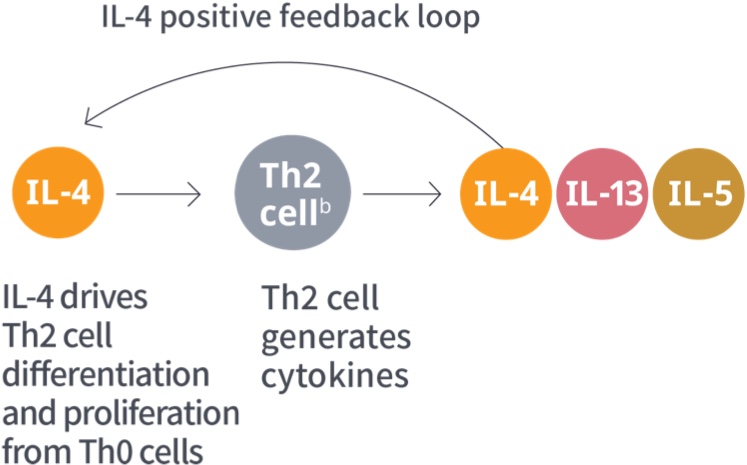
Role of Type 2 cytokines in
atopic dermatitis1,a
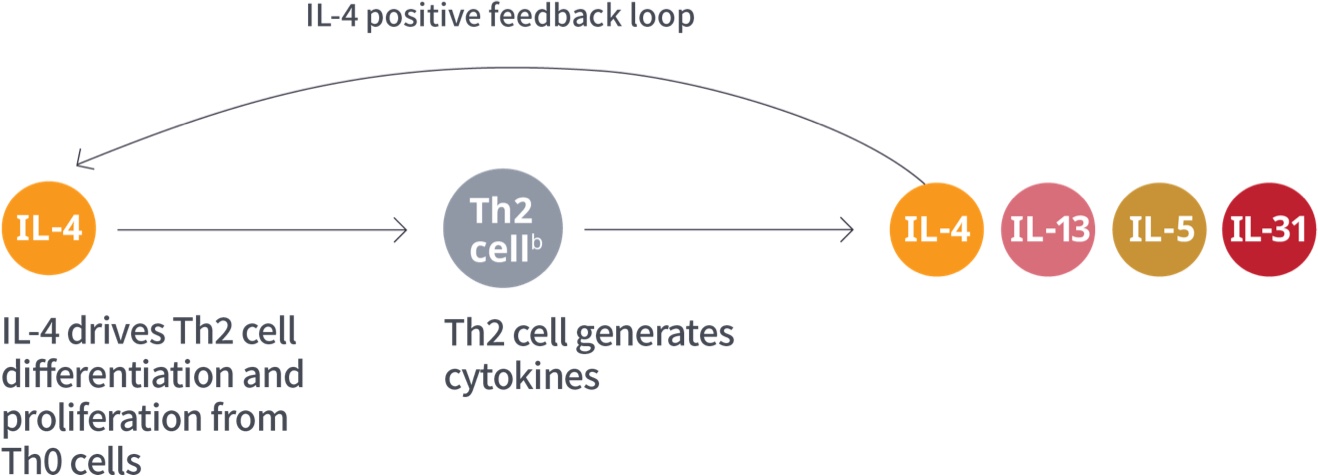
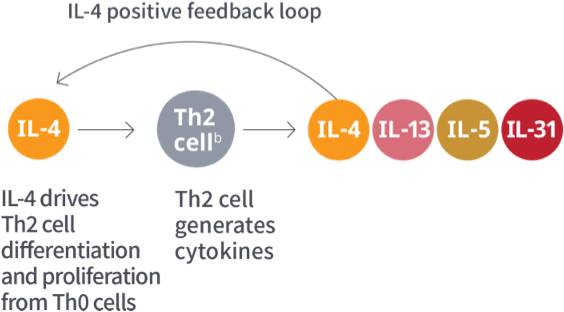
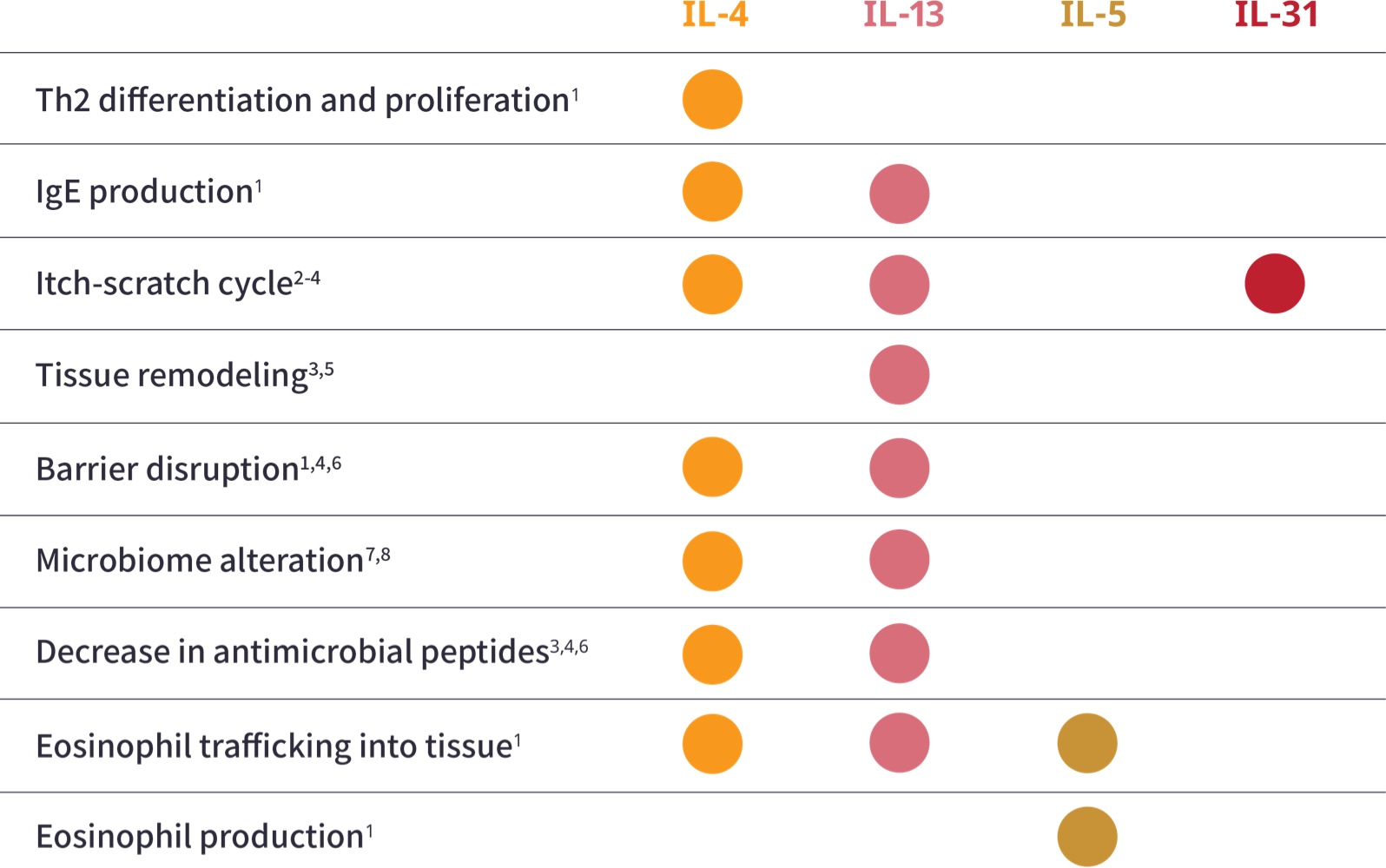
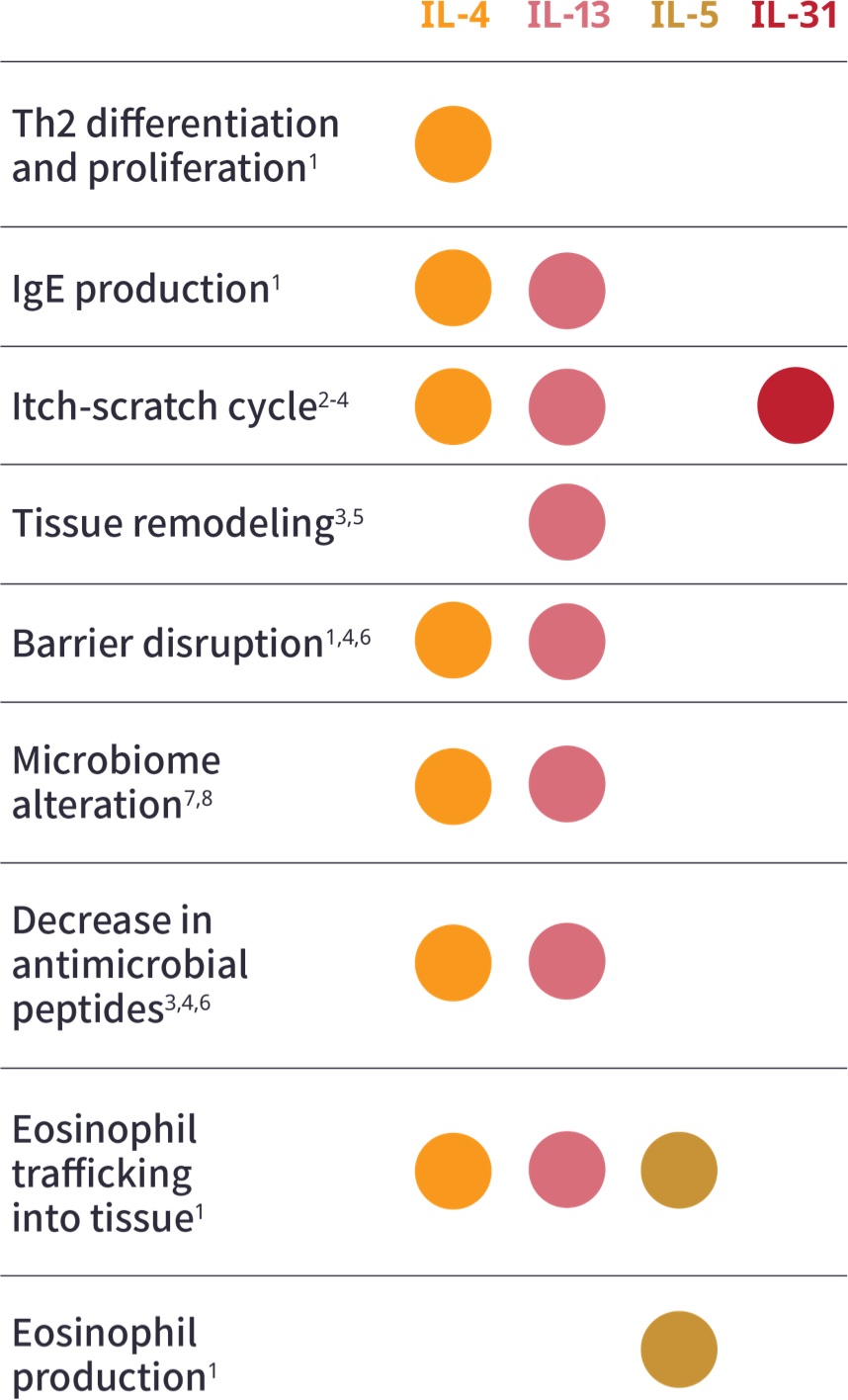
aAdditional Type 2 inflammatory mediators include TSLP, IL-25, and IL-33.1,4
bILC2 cells are an alternate source of IL-13 and IL-5.9
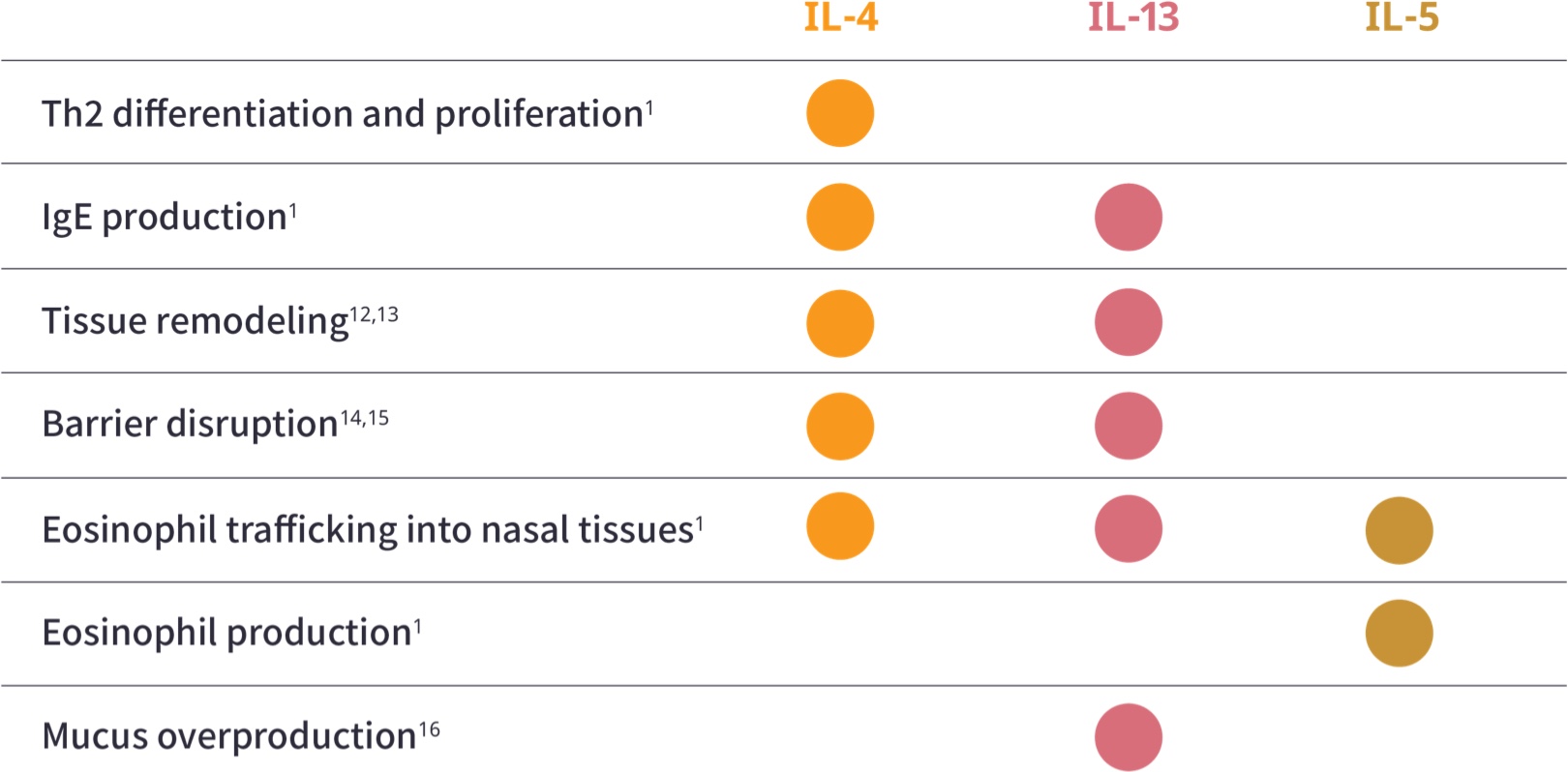
Role of Type 2
cytokines in asthma1,a
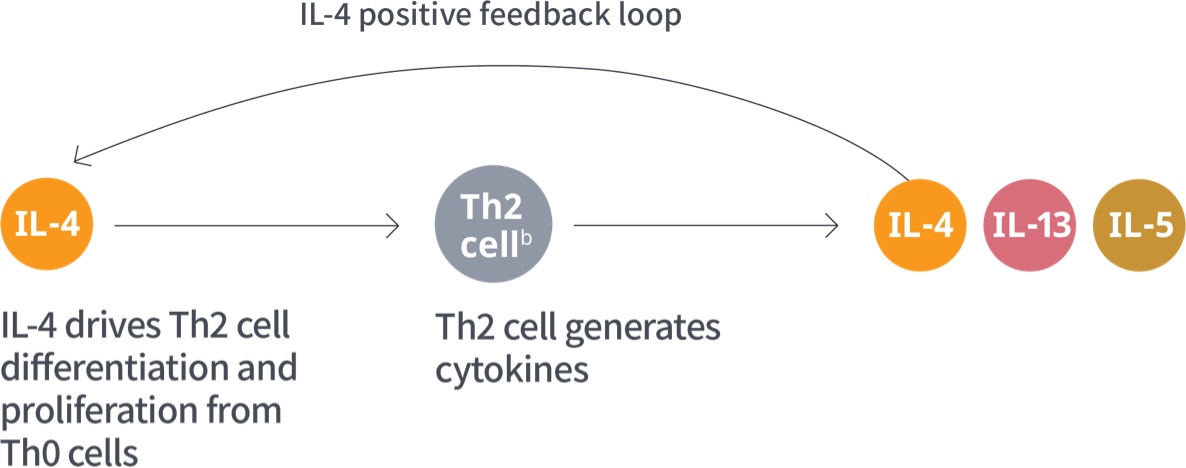
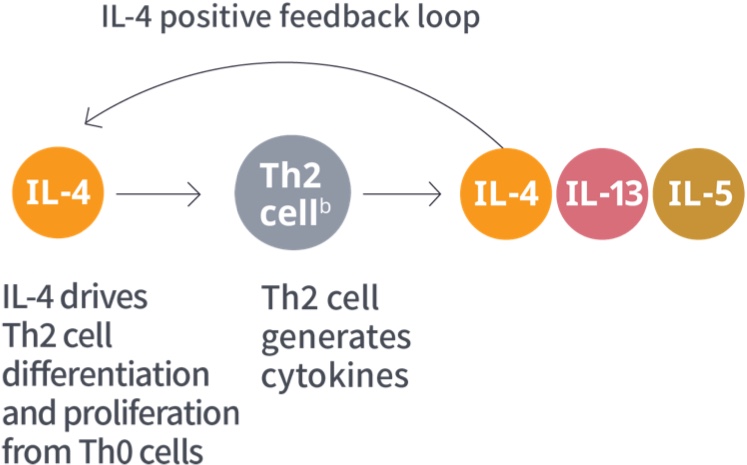
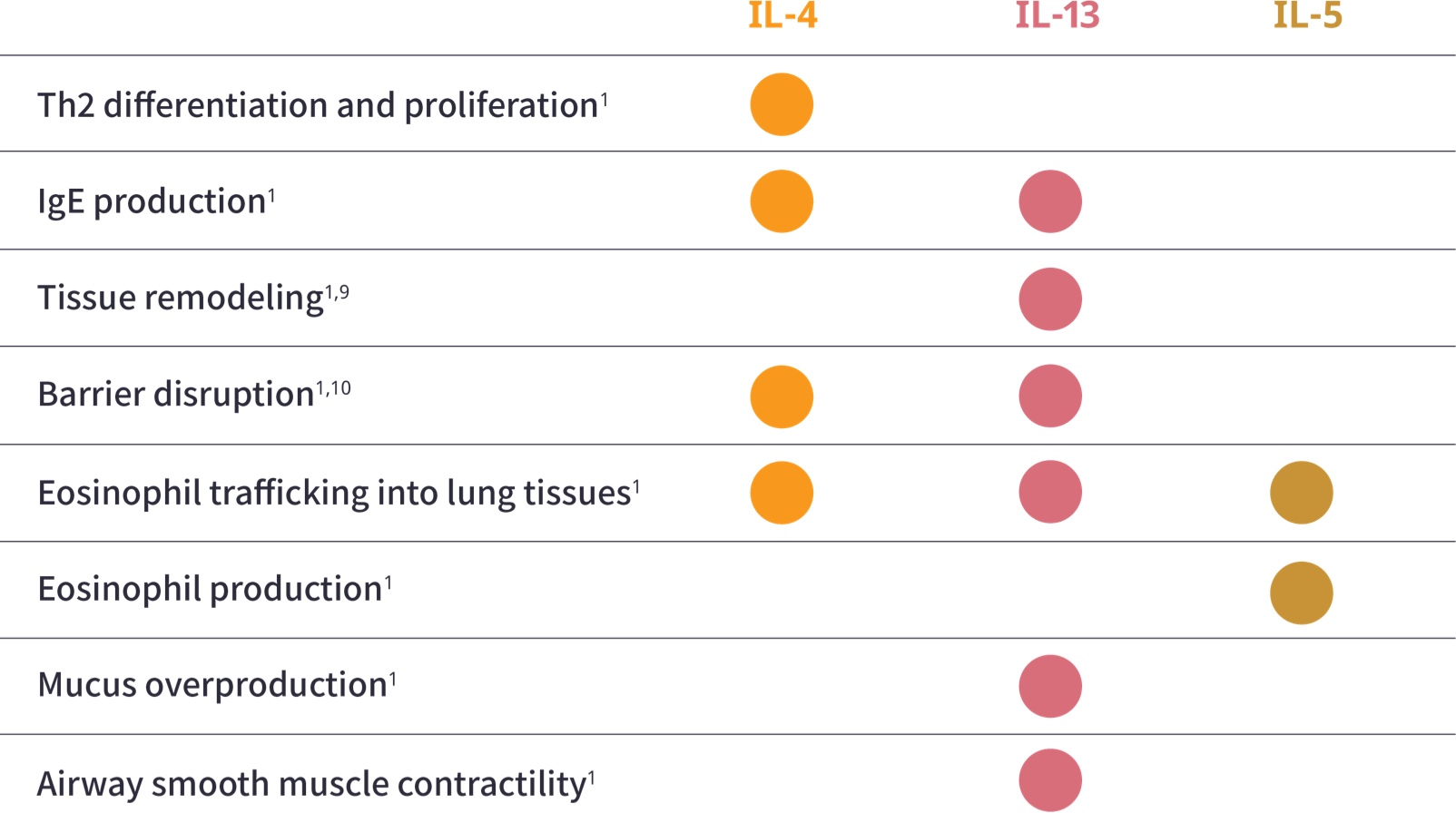
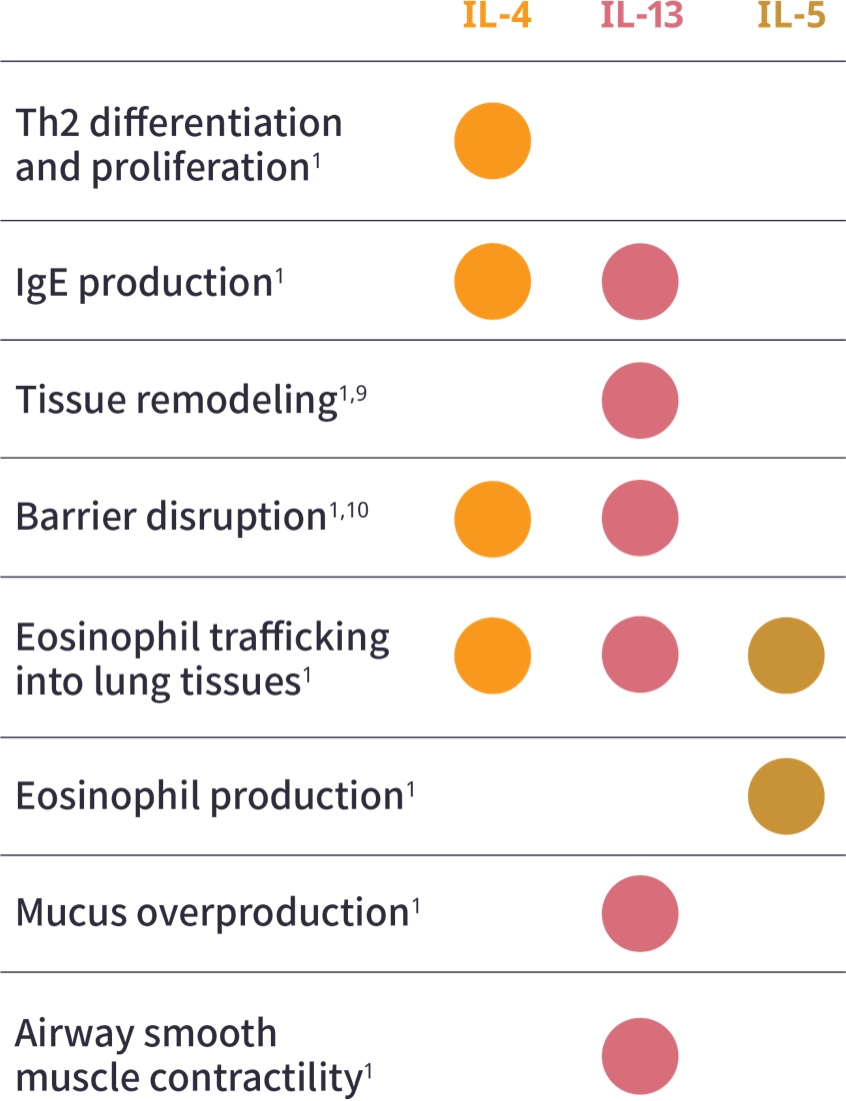
aAdditional Type 2 inflammatory mediators include TSLP, IL-25, and IL-33.1
bILC2 cells are an alternate source of IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5.9,11
Role of Type 2
cytokines in CRSwNP1,a

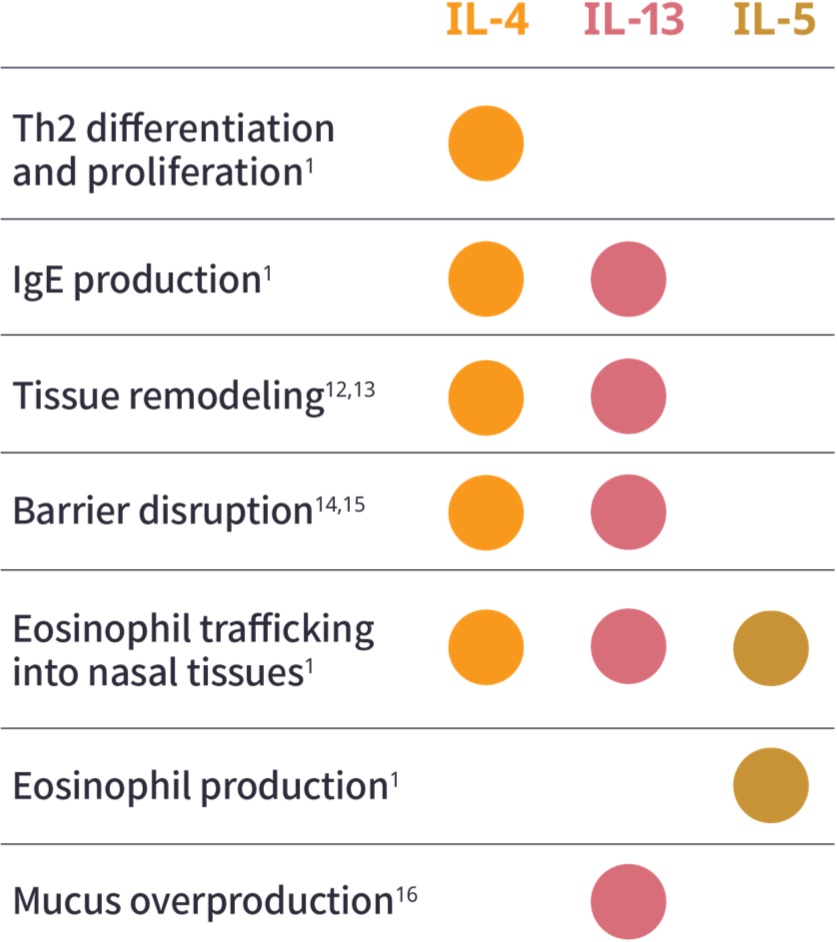
aAdditional Type 2 inflammatory mediators include TSLP, IL-25, and IL-33.1
bILC2 cells are an alternate source of IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5.9,11
Jak Enzymes and
Cytokines
Barrier Dysfunction
in Different Diseases
CRSwNP=chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis; IgE=immunoglobulin E; IL=interleukin; ILC=innate lymphoid cell; Jak=Janus kinase; Th0=T helper cell 0;
Th2=T helper cell 2; TSLP=thymic stromal lymphopoietin.
References
Gandhi NA, Bennett BL, Graham NM, Pirozzi G, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD. Targeting key proximal drivers of Type 2 inflammation in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15(1):35-50.
Stott B, Lavender P, Lehmann S, Pennino D, Durham S, Schmidt-Weber CB. Human IL-31 is induced by IL-4 and promotes TH2-driven inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132(2):446-454.
Brandt EB, Sivaprasad U. Th2 cytokines and atopic dermatitis. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2011;2(3):110. doi:10.4172/2155-9899.1000110
Noda S, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E. The translational revolution and use of biologics in patients with inflammatory skin diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135(2):324-336.
Zheng T, Oh MH, Oh SY, Schroeder JT, Glick AB, Zhu Z. Transgenic expression of interleukin-13 in the skin induces a pruritic dermatitis and skin remodeling. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129(3):742-751.
Hönzke S, Wallmeyer L, Ostrowski A, et al. Influence of Th2 cytokines on the cornified envelope, tight junction proteins, and β-defensins in filaggrin-deficient skin equivalents. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136(3):631-639.
Biedermann T, Skabytska Y, Kaesler S, Volz T. Regulation of T cell immunity in atopic dermatitis by microbes: the yin and yang of cutaneous inflammation. Front Immunol. 2015;6:353. doi:10.3389/ fimmu.2015.00353
Bieber T. Interleukin-13: targeting an underestimated cytokine in atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2020;75(1):54-62.
Robinson D, Humbert M, Buhl R, et al. Revisiting Type 2-high and Type 2-low airway inflammation in asthma: current knowledge and therapeutic implications. Clin Exp Allergy. 2017;47(2):161-175.
Saatian B, Rezaee F, Desando S, et al. Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 cause barrier dysfunction in human airway epithelial cells. Tissue Barriers. 2013;1(2):e24333. doi:10.4161/tisb.24333
Boonpiyathad T, Sözener ZC, Satitsuksanoa P, Akdis CA. Immunologic mechanisms in asthma. Semin Immunol. 2019;46:101333. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2019.101333
Kato A. Immunopathology of chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol Int. 2015;64(2):121-130.
Tomlinson KL, Davies GCG, Sutton DJ, Palframan RT. Neutralisation of interleukin-13 in mice prevents airway pathology caused by chronic exposure to house dust mite. PLoS One. 2010;5(10):e13136. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013136
Soyka MB, Wawrzyniak P, Eiwegger T, et al. Defective epithelial barrier in chronic rhinosinusitis: the regulation of tight junctions by IFN-γ and IL-4. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130(5):1087‐1096.
Wise SK, Laury AM, Katz EH, Den Beste KA, Parkos CA, Nusrat A. IL-4 and IL-13 compromise the sinonasal epithelial barrier and perturb intercellular junction protein expression. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014;4(5):361-370.
Jiao J, Duan S, Meng N, Li Y, Fan E, Zhang L. Role of IFN-γ, IL-13, and IL-17 on mucociliary differentiation of nasal epithelial cells in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016;46(3):449-460.
IMM.20.10.0003 Last Update: [12/20]
© 2021 Sanofi and Regeneron
Pharmaceuticals, Inc. All Rights Reserved.

